Romans name for spain crossword clue – Unraveling the crossword clue “Roman name for Spain” embarks us on a captivating journey through the annals of history, linguistics, and cultural exchange. This enigmatic name, “Hispania,” has left an enduring mark on the Iberian Peninsula, shaping its identity and heritage.
The Roman conquest of Spain marked a pivotal chapter in the region’s history, introducing a profound influence on its culture, language, and infrastructure. The name “Hispania” emerged from this transformative period, becoming an enduring testament to Roman dominance.
Historical Context
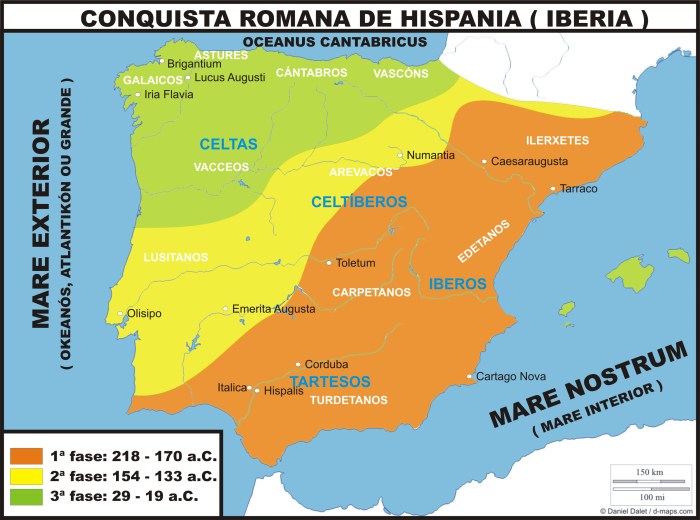
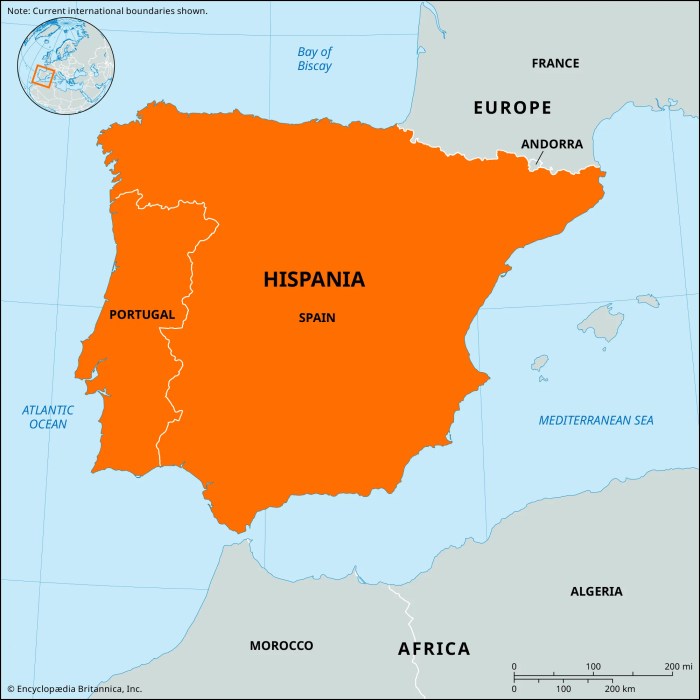
The Roman Empire’s expansion into the Iberian Peninsula, known as Hispania, was a significant event in the region’s history. The conquest and occupation of Spain by the Romans had a profound impact on the peninsula’s culture, language, and infrastructure.
Roman Conquest and Occupation
The Roman conquest of Hispania began in the 3rd century BCE and was completed by the 1st century BCE. The Romans divided the peninsula into several provinces, including Tarraconensis, Baetica, and Lusitania. The region became an important part of the Roman Empire, providing agricultural products, minerals, and manpower.
Impact of Roman Rule
Roman rule had a lasting impact on Spain. The Romans introduced a system of law and government, which formed the basis of Spanish legal and political systems. They also built roads, bridges, and aqueducts, which improved transportation and communication. The Romans also introduced Christianity to Spain, which became the dominant religion in the region.
Cultural Influence
The Roman conquest also had a significant impact on Spanish culture. The Romans introduced their language, Latin, which became the official language of Spain. They also introduced their art, architecture, and literature, which influenced Spanish culture for centuries to come.
Etymology and Language
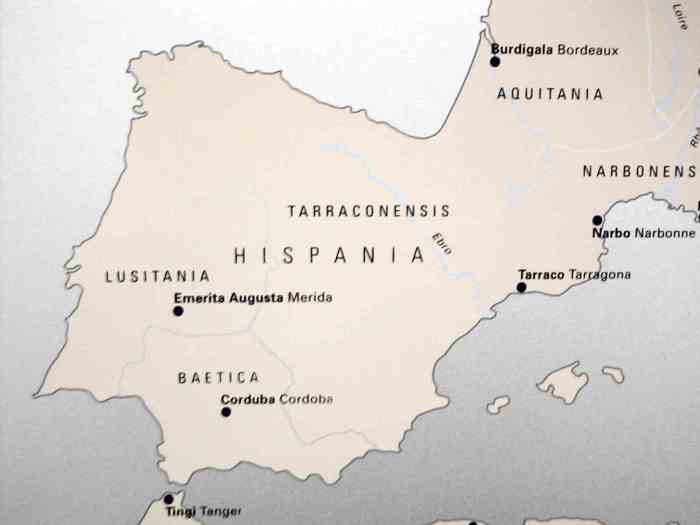
The Roman name for Spain, “Hispania,” has a complex etymological history. The name likely originated from the Phoenician word “Span,” meaning “hidden” or “distant,” as the region was seen as a remote and mysterious land to the Phoenicians. Over time, the name evolved into “Hispania” in Latin, which became the official Roman designation for the Iberian Peninsula.
The name “Hispania” underwent further linguistic evolution during the Roman period. It was often used in conjunction with other terms to denote specific regions within the peninsula, such as “Hispania Citerior” (Nearer Spain) and “Hispania Ulterior” (Farther Spain). After the fall of the Roman Empire, the name “Hispania” continued to be used by the Visigoths and other Germanic tribes who ruled the region.
It eventually evolved into the modern Spanish name “España” and the Portuguese name “Espanha.”
Modern-Day Spanish Language and Culture
The name “Hispania” has left a lasting legacy in modern-day Spanish language and culture. It is reflected in numerous place names, such as the Spanish provinces of “Castilla y León” (Land of Castles and Lions) and “Extremadura” (Land of the Extreme).
The name is also used in the Spanish national anthem, “Marcha Real,” which includes the line “Viva España” (Long live Spain).
Geographic and Political Divisions
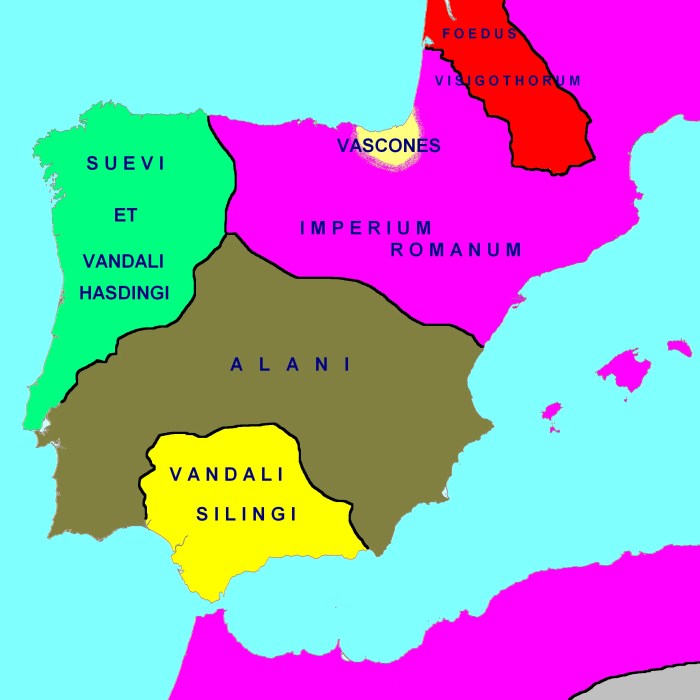
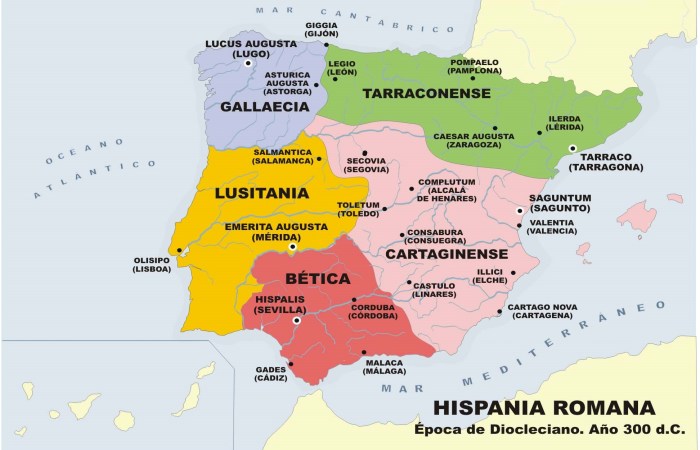
Roman Hispania, encompassing the Iberian Peninsula and parts of southern Gaul, was a vast and diverse territory. It was divided into several provinces, each with its own administrative center:
Provinces
- Tarraconensis: The largest province, covering the northeastern part of the peninsula, with its capital at Tarraco (modern Tarragona).
- Baetica: In the south, with its capital at Corduba (modern Cordoba).
- Lusitania: In the west, with its capital at Emerita Augusta (modern Merida).
- Carthaginensis: In the southeast, with its capital at Carthago Nova (modern Cartagena).
Major cities in Hispania included:
Major Cities
- Corduba: The provincial capital of Baetica and the largest city in Hispania, renowned for its wealth and cultural significance.
- Hispalis(modern Seville): A major port city in Baetica, known for its trade and shipbuilding.
- Emerita Augusta: The provincial capital of Lusitania, founded as a veteran colony and later became a flourishing city.
- Tarraco: The provincial capital of Tarraconensis, a strategic port and commercial center.
- Carthago Nova: The provincial capital of Carthaginensis, a major naval base and trading hub.
Hispania played a crucial role in the Roman Empire’s defense and trade networks. Its strategic location at the western end of the Mediterranean Sea made it a vital gateway to the Atlantic and beyond. Hispania supplied the empire with valuable resources, such as gold, silver, and agricultural products, and served as a base for military campaigns in northern Africa and Gaul.
Cultural Influences
The Roman Empire’s extensive influence on Spain left a profound legacy that continues to shape the nation’s culture, society, and identity. The Romans introduced a plethora of cultural elements, ranging from architecture and art to religion and law, which deeply embedded themselves into the fabric of Spanish society.
One of the most enduring legacies of Roman culture in Spain is its architectural heritage. Roman cities, such as Tarraco (present-day Tarragona), Emerita Augusta (Mérida), and Corduba (Córdoba), showcase the grandeur and engineering prowess of the empire. The ruins of Roman amphitheaters, aqueducts, and temples can still be found throughout the country, serving as testaments to the Romans’ architectural ingenuity.
Art and Culture
Roman art also left a lasting impact on Spain. The Romans introduced a variety of artistic styles, including mosaics, frescoes, and sculptures, which adorned public spaces and private homes. Many of these works depict scenes from Roman mythology, history, and daily life, providing valuable insights into the Roman worldview.
In addition to architecture and art, the Romans also brought their religion to Spain. The Roman pantheon, including gods such as Jupiter, Juno, and Minerva, was adopted by the local population, and many Roman temples were converted into Christian churches.
The influence of Roman religion can still be seen in the use of Latin in the Catholic Church and the presence of Romanesque architectural elements in many Spanish cathedrals.
Law and Society
The Roman legal system also had a profound impact on Spanish society. The Romans introduced a codified system of law, known as the Twelve Tables, which established a framework for civil and criminal justice. This system formed the basis for subsequent legal systems in Spain and throughout Europe.
The Roman Empire’s cultural legacy continues to permeate Spanish society today. Roman architecture, art, religion, and law have all left an indelible mark on the nation’s identity. These cultural influences have shaped Spain’s cultural landscape and continue to inspire and inform Spanish culture.
Archaeological Evidence: Romans Name For Spain Crossword Clue

Spain’s rich archaeological heritage offers tangible evidence of Roman occupation, providing valuable insights into the daily lives, culture, and political organization of Roman Hispania. Through meticulous excavations and advanced scientific techniques, archaeologists have unearthed a wealth of artifacts, structures, and inscriptions that illuminate the Roman era.
Significant Archaeological Sites
Numerous archaeological sites in Spain attest to the profound impact of Roman rule. Among the most significant are:
- Tarraco (modern Tarragona): The former capital of Hispania Tarraconensis, Tarraco boasts impressive Roman ruins, including an amphitheater, aqueduct, and forum.
- Emerita Augusta (modern Mérida): This well-preserved Roman city in western Spain showcases a magnificent aqueduct, a stone bridge, and a Roman theater.
- Baelo Claudia (modern Bolonia): Situated on the southern coast, Baelo Claudia is a fascinating Roman port city with well-preserved streets, houses, and a fish-salting factory.
li> Complutum (modern Alcalá de Henares): Located near Madrid, Complutum offers a glimpse into a Roman settlement, with excavated houses, baths, and a basilica.
Excavation and Study Methods
Archaeological excavations in Spain employ a range of scientific techniques to uncover and analyze Roman sites. These methods include:
- Stratigraphic excavation: Digging in layers to reveal the chronological sequence of occupation.
- Remote sensing: Using non-invasive techniques like ground-penetrating radar to detect buried structures and artifacts.
- Artifact analysis: Studying pottery, coins, tools, and other objects to identify their function and cultural significance.
- Epigraphic analysis: Examining inscriptions on stone tablets, monuments, and other surfaces to gain insights into Roman administration and daily life.
Contribution to Understanding Roman Hispania
Archaeological findings in Spain have greatly enriched our understanding of Roman Hispania. They have provided evidence of:
- Roman urban planning: The layout of cities like Tarraco and Mérida reflects Roman principles of grid systems, public spaces, and infrastructure.
- Economic activities: Excavated pottery, coins, and other artifacts reveal the importance of agriculture, trade, and mining in Roman Hispania.
- Cultural influences: Roman architecture, art, and religion left a lasting impact on the region, as evidenced by temples, mosaics, and inscriptions.
- Political organization: The discovery of Roman administrative documents and inscriptions sheds light on the governance and legal system of Hispania.
Contemporary Relevance
The Roman name for Spain, “Hispania,” continues to resonate in contemporary Spanish culture, influencing national identity, cultural heritage, and artistic expression.
Literature, Art, and Popular Culture, Romans name for spain crossword clue
The name “Hispania” frequently appears in modern Spanish literature, art, and popular culture, evoking a sense of historical connection and national pride. For example, the renowned Spanish poet Federico García Lorca used the term in his poem “Romance de la Guardia Civil Española,” which depicts the struggle between the Spanish people and the oppressive regime of the time.
FAQs
What is the origin of the name “Hispania”?
The name “Hispania” is derived from the Carthaginian term “Spania,” which likely originated from the Phoenician word “Span,” meaning “hidden” or “remote.”
What was the geographic extent of Roman Hispania?
Roman Hispania encompassed the entire Iberian Peninsula, including present-day Spain and Portugal, as well as parts of southern France.
What are some examples of Roman cultural influences on Spain?
Roman cultural influences on Spain include architecture (e.g., aqueducts, amphitheaters), art (e.g., mosaics, sculptures), religion (e.g., Christianity), and law (e.g., the Roman legal system).