Welcome to the world of protein synthesis, where the intricate dance of DNA, RNA, and ribosomes unfolds, giving life to the proteins that orchestrate every aspect of cellular function. In this comprehensive guide, we present protein synthesis flow chart answers, unlocking the secrets of this fundamental biological process.
Delve into the molecular machinery that governs protein synthesis, from the initial transcription of DNA to the final translation of mRNA into functional proteins. Discover the key steps, the players involved, and the regulatory mechanisms that ensure the precise synthesis of proteins essential for life.
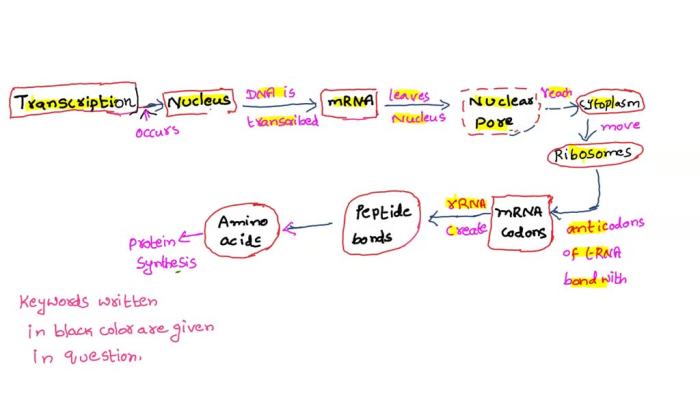
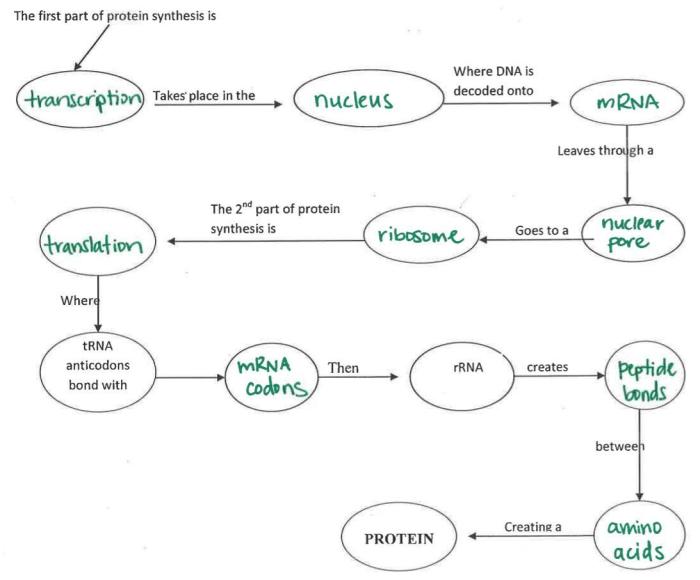
Protein Synthesis Overview
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create proteins, essential molecules that perform a wide range of functions within the body. It involves two main stages: transcription and translation.
Transcription
Transcription is the process of copying the genetic information from DNA into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. This process is carried out by an enzyme called RNA polymerase, which binds to the DNA and uses it as a template to create a complementary mRNA molecule.
Translation, Protein synthesis flow chart answers
Translation is the process of converting the mRNA molecule into a protein. This process occurs on ribosomes, which are large, complex structures found in the cytoplasm. The ribosome binds to the mRNA molecule and uses it as a template to assemble a chain of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
Regulation of Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is a highly regulated process, ensuring that cells produce the right proteins at the right time. This regulation is achieved through a variety of mechanisms, including transcription factors and post-translational modifications.
FAQ Overview: Protein Synthesis Flow Chart Answers
What is the role of DNA in protein synthesis?
DNA serves as the genetic blueprint, providing the instructions for protein synthesis. It contains the nucleotide sequence that encodes the amino acid sequence of the protein.
How does transcription differ from translation?
Transcription involves the synthesis of mRNA from a DNA template, while translation involves the synthesis of proteins from mRNA.
What are the key steps of translation?
Translation involves initiation, elongation, and termination, during which ribosomes read the mRNA sequence and assemble amino acids into a polypeptide chain.