Primary succession and secondary succession venn diagram – The concept of primary and secondary succession is a cornerstone in ecology, explaining the dynamic processes of ecosystem development. This article delves into the intricacies of primary and secondary succession, utilizing a Venn diagram to elucidate their similarities and differences.
Primary and Secondary Succession
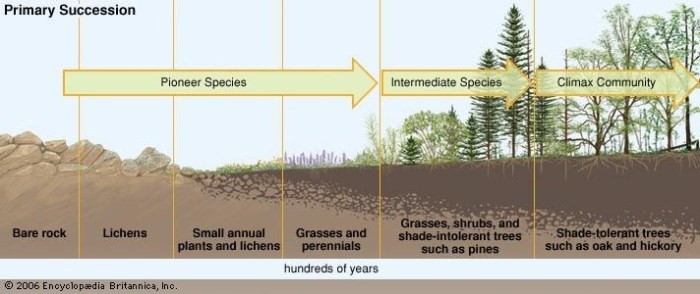
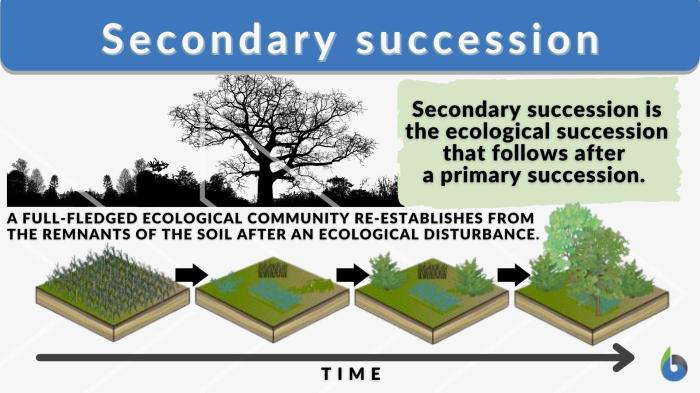
Succession is a gradual change in the composition of a biological community over time. Primary succession occurs on newly exposed or created land, while secondary succession occurs on land that has been disturbed but still has some existing vegetation.
Definitions
Primary Succession
Primary succession occurs on land that has never been vegetated before, such as a newly formed volcanic island or a glacier-scoured landscape. The first organisms to colonize these areas are typically small, hardy plants like lichens and mosses. These plants help to break down the rock and create soil, making it possible for larger plants to grow.
Secondary Succession
Secondary succession occurs on land that has been disturbed but still has some existing vegetation. This type of succession can be caused by natural events, such as fire or flooding, or by human activities, such as logging or farming. The early stages of secondary succession are similar to those of primary succession, but the presence of existing vegetation can speed up the process.
Venn Diagram, Primary succession and secondary succession venn diagram
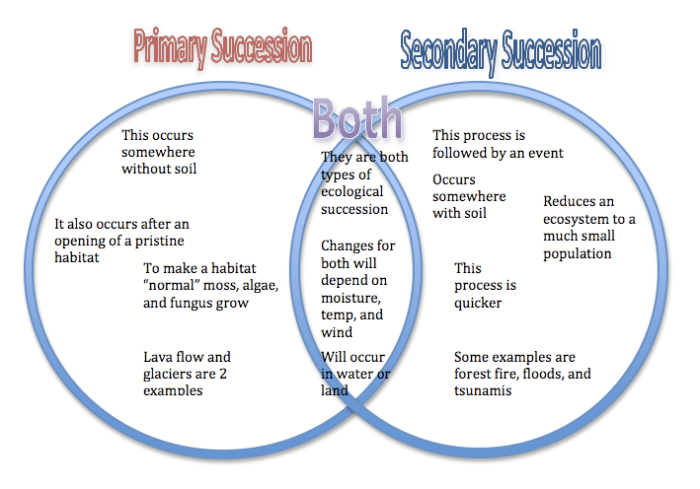
The following Venn diagram compares primary and secondary succession:
| Primary Succession | Secondary Succession | |
|---|---|---|
| Overlapping | – Start with bare ground | – Start with some existing vegetation |
| Non-Overlapping | – Occurs on newly exposed or created land | – Occurs on land that has been disturbed |
Differences
The following are some of the key differences between primary and secondary succession:
- Primary succession starts with bare ground, while secondary succession starts with some existing vegetation.
- Primary succession is a slower process than secondary succession.
- Primary succession leads to the development of a new ecosystem, while secondary succession leads to the recovery of an existing ecosystem.
Similarities
Despite their differences, primary and secondary succession share some similarities:
- Both types of succession involve the gradual change in the composition of a biological community over time.
- Both types of succession are influenced by environmental factors, such as climate and soil conditions.
- Both types of succession can be used to restore damaged ecosystems.
Examples
Primary Succession
A classic example of primary succession is the colonization of a newly formed volcanic island. The first organisms to colonize the island are typically lichens and mosses. These plants help to break down the rock and create soil, making it possible for larger plants to grow.
Over time, a diverse ecosystem develops on the island.
Secondary Succession
A common example of secondary succession is the recovery of a forest after a fire. After a fire, the forest floor is covered with dead trees and ash. However, over time, new plants begin to grow in the burned area.
These plants eventually grow into a new forest.
Applications
Understanding primary and secondary succession is important for a number of reasons:
- It can help us to understand how ecosystems recover from natural and human-caused disturbances.
- It can help us to restore damaged ecosystems.
- It can help us to predict how climate change will affect ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions: Primary Succession And Secondary Succession Venn Diagram
What is the primary distinction between primary and secondary succession?
Primary succession occurs on previously barren or devoid substrates, while secondary succession initiates on sites that have experienced disturbance but retain some residual soil and organic matter.
How does the rate of succession differ between primary and secondary succession?
Primary succession is typically slower than secondary succession due to the lack of existing soil and organic matter, which provide nutrients and support for plant establishment.
Can secondary succession lead to the reestablishment of the original ecosystem?
In some cases, secondary succession can restore the original ecosystem, but this depends on factors such as the severity of the disturbance, the availability of propagules, and the resilience of the ecosystem.