Which of the following statements about groundwater is false? This question may seem simple, but the answer can be surprisingly complex. Groundwater is a vast and complex resource that is essential for human life. However, it is also a resource that is under increasing pressure from pollution, climate change, and other factors.
In this article, we will explore the different statements about groundwater and determine which one is false.
Groundwater is found beneath the Earth’s surface in aquifers, which are layers of rock or soil that hold water. Aquifers can be found at different depths, and they can vary in size from small, local aquifers to large, regional aquifers.
Groundwater is an important source of drinking water for many people around the world. It is also used for irrigation, industry, and other purposes.
Overview of Groundwater
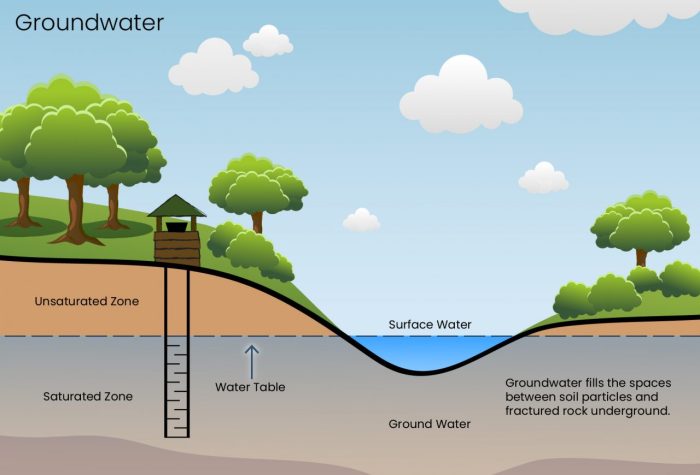
Groundwater is the water found beneath the Earth’s surface in the spaces between soil particles and the cracks and pores of rock formations. It is a vital natural resource that plays a crucial role in the global water cycle and provides a significant source of drinking water for many communities worldwide.
Occurrence and Distribution, Which of the following statements about groundwater is false
Groundwater occurs in aquifers, which are underground geological formations that contain and transmit water. Aquifers can be composed of various materials, such as sand, gravel, limestone, and sandstone. The distribution and availability of groundwater vary depending on factors like geology, climate, and human activities.
Importance as a Resource
Groundwater is an essential resource for human consumption, irrigation, and industrial processes. It is often a reliable and consistent water source, especially during droughts or in areas with limited surface water availability. Additionally, groundwater provides baseflow to rivers and wetlands, maintaining aquatic ecosystems and supporting biodiversity.
Properties of Groundwater
Physical and Chemical Properties
Groundwater typically has a lower temperature than surface water due to its isolation from the atmosphere. It can vary in chemical composition depending on the geological formations it flows through. Common dissolved minerals in groundwater include calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, and bicarbonate.
Factors Influencing Groundwater Quality
Groundwater quality can be influenced by various factors, including the composition of the aquifer materials, human activities (such as industrial discharges and agricultural practices), and natural processes (such as weathering and biological activity).
Significance for Various Uses
The quality of groundwater is critical for its various uses. For drinking purposes, groundwater should meet specific standards for contaminants and microorganisms. For irrigation, groundwater salinity and pH levels are important considerations. Industrial processes may require specific water quality parameters, such as hardness or mineral content.
Groundwater Movement
Principles of Groundwater Flow
Groundwater moves through aquifers under the influence of gravity and pressure gradients. Water flows from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure, following Darcy’s Law. The hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer material determines the rate of groundwater flow.
Factors Affecting Groundwater Movement
Factors that influence groundwater movement include aquifer properties (e.g., porosity and permeability), recharge rates, discharge mechanisms, and human activities (e.g., pumping from wells).
Role in the Water Cycle
Groundwater plays a crucial role in the water cycle by connecting surface water bodies and providing baseflow during dry periods. It also contributes to the recharge of surface water bodies and the maintenance of aquatic ecosystems.
Groundwater Recharge and Discharge
Processes of Groundwater Recharge
Groundwater is primarily recharged through precipitation (infiltration), snowmelt, and surface water bodies (e.g., rivers and lakes) that seep into the ground. Recharge rates vary depending on factors such as soil permeability, land use, and climate.
Mechanisms of Groundwater Discharge
Groundwater is discharged through natural processes such as springs, seeps, and evapotranspiration. Human activities, including pumping from wells, can also contribute to groundwater discharge.
Importance for Groundwater Sustainability
Understanding recharge and discharge processes is crucial for sustainable groundwater management. Balancing groundwater withdrawals with recharge rates ensures the long-term availability of this vital resource.
Groundwater Management: Which Of The Following Statements About Groundwater Is False

Challenges
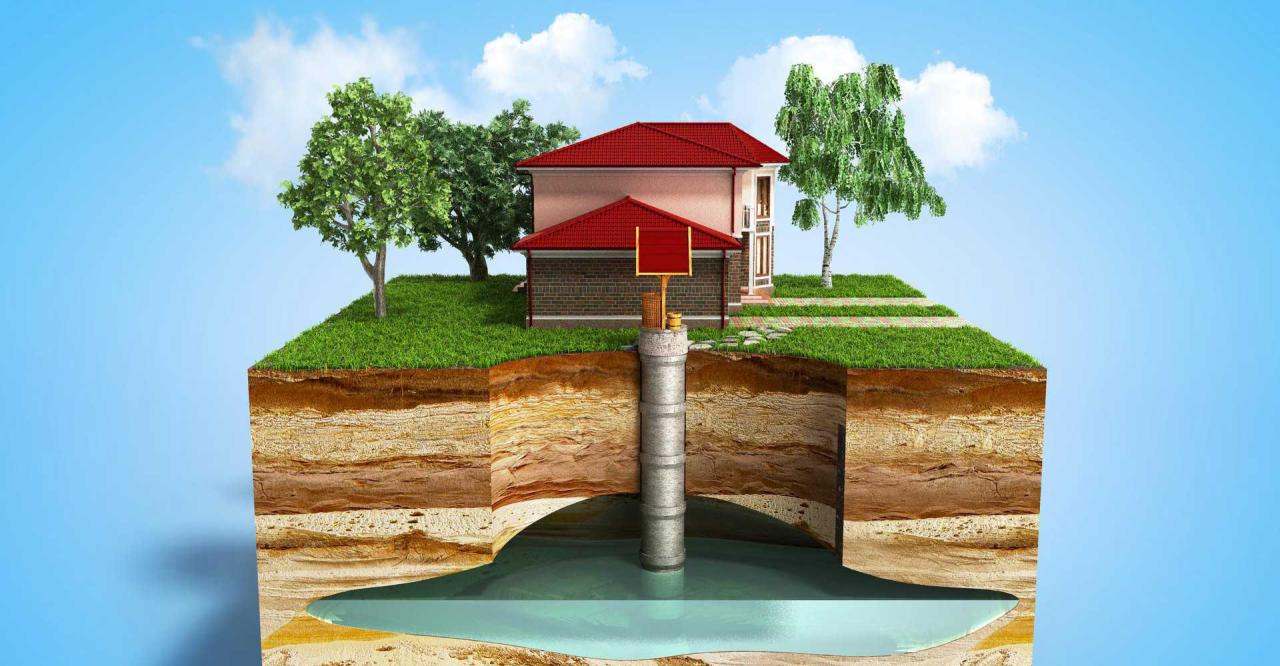
Groundwater management faces challenges such as over-extraction, contamination, and climate change impacts. Managing groundwater resources sustainably requires a comprehensive understanding of aquifer systems and careful planning.
Strategies and Techniques
Groundwater management strategies include monitoring groundwater levels, regulating pumping rates, implementing recharge enhancement measures, and protecting groundwater quality. Advanced technologies, such as numerical modeling and remote sensing, can aid in effective groundwater management.
Importance of Sustainable Groundwater Use
Sustainable groundwater use involves balancing withdrawals with recharge rates and minimizing the environmental impacts of groundwater extraction. It ensures the long-term availability of this vital resource for future generations.
Groundwater Contamination

Sources and Types
Groundwater contamination can occur from various sources, including industrial discharges, agricultural practices, septic systems, and landfills. Contaminants can include heavy metals, pesticides, solvents, and bacteria.
Processes and Impacts
Groundwater contamination can result in the degradation of water quality, posing risks to human health and ecosystems. It can also affect the availability and usability of groundwater resources.
Methods for Prevention and Remediation
Preventing and remediating groundwater contamination involves implementing best management practices, regulating potential sources of contamination, and employing technologies for cleanup and restoration.
Groundwater and Climate Change
Potential Impacts
Climate change is expected to impact groundwater resources through changes in precipitation patterns, temperature, and sea level rise. These impacts can affect groundwater recharge, discharge, and quality.
Role in Mitigation
Groundwater can play a role in mitigating the effects of climate change by providing a reliable water source during droughts and helping to regulate temperatures in urban areas.
Adaptation Strategies
Adapting groundwater management to climate change involves monitoring and predicting changes, implementing flexible management strategies, and investing in research and development to enhance groundwater resilience.
Expert Answers
What is groundwater?
Groundwater is water that is found beneath the Earth’s surface in aquifers, which are layers of rock or soil that hold water.
What is the importance of groundwater?
Groundwater is an important source of drinking water for many people around the world. It is also used for irrigation, industry, and other purposes.
What are the threats to groundwater?
Groundwater is under increasing pressure from pollution, climate change, and other factors.